- Classification of major climatic types according to the Koppen-Geiger-Pohl scheme
-
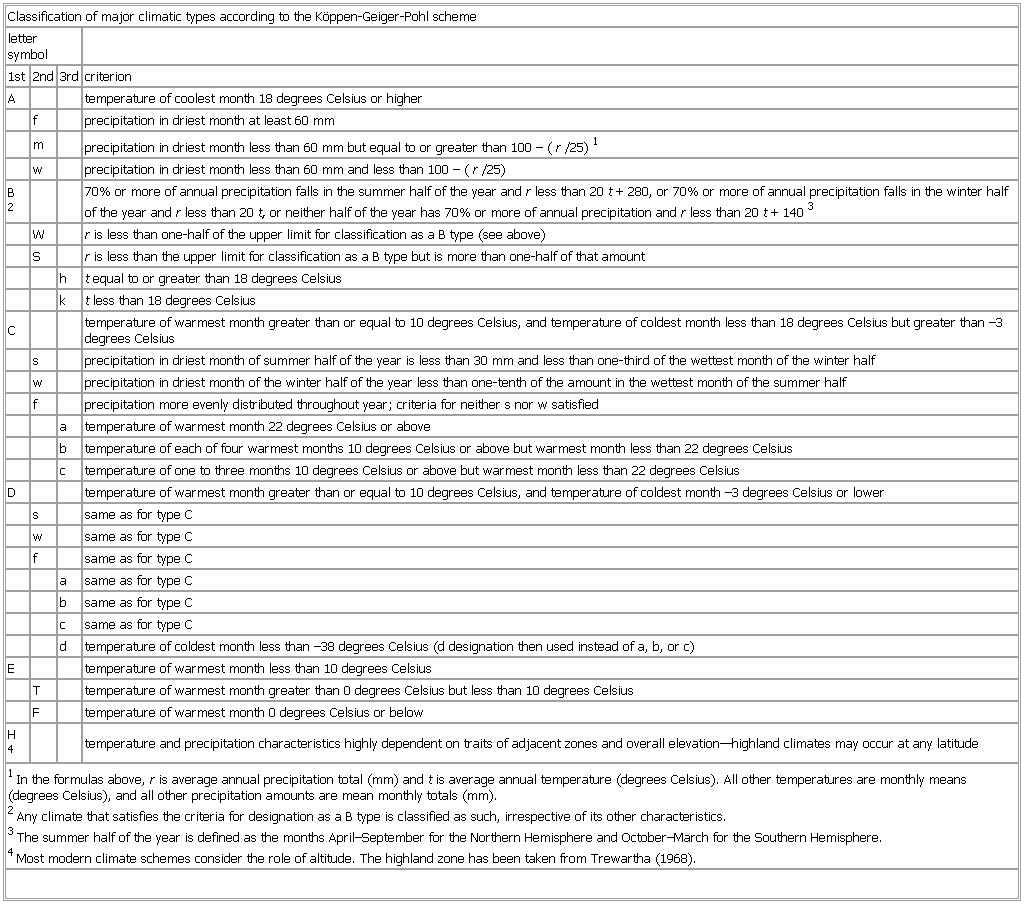
▪ TableClassification of major climatic types according to the Köppen-Geiger-Pohl schemeletter symbol1st 2nd 3rd criterionA temperature of coolest month 18 degrees Celsius or higherf precipitation in driest month at least 60 mmm precipitation in driest month less than 60 mm but equal to or greater than 100 – (r/25)1w precipitation in driest month less than 60 mm and less than 100 – (r/25)B2 70% or more of annual precipitation falls in the summer half of the year and r less than 20t + 280, or 70% or more of annual precipitation falls in the winter half of the year and r less than 20t, or neither half of the year has 70% or more of annual precipitation and r less than 20t + 1403W r is less than one-half of the upper limit for classification as a B type (see above)S r is less than the upper limit for classification as a B type but is more than one-half of that amounth t equal to or greater than 18 degrees Celsiusk t less than 18 degrees CelsiusC temperature of warmest month greater than or equal to 10 degrees Celsius, and temperature of coldest month less than 18 degrees Celsius but greater than –3 degrees Celsiuss precipitation in driest month of summer half of the year is less than 30 mm and less than one-third of the wettest month of the winter halfw precipitation in driest month of the winter half of the year less than one-tenth of the amount in the wettest month of the summer halff precipitation more evenly distributed throughout year; criteria for neither s nor w satisfieda temperature of warmest month 22 degrees Celsius or aboveb temperature of each of four warmest months 10 degrees Celsius or above but warmest month less than 22 degrees Celsiusc temperature of one to three months 10 degrees Celsius or above but warmest month less than 22 degrees CelsiusD temperature of warmest month greater than or equal to 10 degrees Celsius, and temperature of coldest month –3 degrees Celsius or lowers same as for type Cw same as for type Cf same as for type Ca same as for type Cb same as for type Cc same as for type Cd temperature of coldest month less than –38 degrees Celsius (d designation then used instead of a, b, or c)E temperature of warmest month less than 10 degrees CelsiusT temperature of warmest month greater than 0 degrees Celsius but less than 10 degrees CelsiusF temperature of warmest month 0 degrees Celsius or belowH4 temperature and precipitation characteristics highly dependent on traits of adjacent zones and overall elevation—highland climates may occur at any latitude1In the formulas above, r is average annual precipitation total (mm) and t is average annual temperature (degrees Celsius). All other temperatures are monthly means (degrees Celsius), and all other precipitation amounts are mean monthly totals (mm).2Any climate that satisfies the criteria for designation as a B type is classified as such, irrespective of its other characteristics.3The summer half of the year is defined as the months April–September for the Northern Hemisphere and October–March for the Southern Hemisphere.4Most modern climate schemes consider the role of altitude. The highland zone has been taken from Trewartha (1968).See as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
