Human Spaceflight Launches and Returns, 2003
- Human Spaceflight Launches and Returns, 2003
-
William McCool
Michael Anderson
Kalpana Chawla
David Brown
Laurel Clark
Ilan Ramon January 16-February 1 space experiments in biological and physical sciences;
Columbia destroyed during return to Earth
Russia Soyuz TMA-2 (
up) Yury Malenchenko
Edward Lu April 26 transport of replacement crew to ISS
Russia Soyuz TMA-1 (
down) Ken Bowersox
Nikolay Budarin
Donald Pettit May 4 return of departing ISS crew to Earth
China Shenzhou 5 Yang Liwei October 15-16 China's first human spaceflight (21.4 hours, 14 orbits)
Russia Soyuz TMA-3 (
up) Michael Foale
Aleksandr Kaleri
Pedro Duque October 18 transport of replacement crew to ISS
Russia Soyuz TMA-2 (
down) Yury Malenchenko
Edward Lu
Pedro Duque October 28 return of departing ISS crew to Earth
See as table: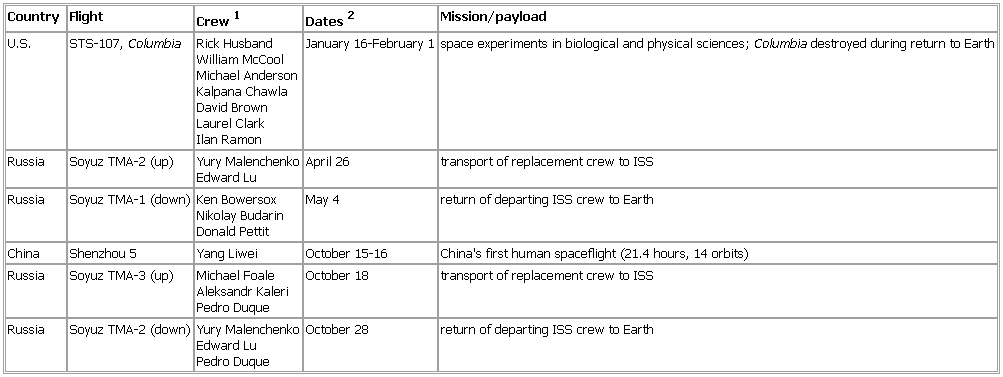
1For shuttle flight, commander and pilot are listed first; for Soyuz flights, ISS commander is listed first.
2Flight dates for shuttle and Shenzhou missions; Soyuz launch or return date for ISS missions.
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Spaceflight — For the magazine published by the British Interplanetary Society, see Spaceflight (magazine). For the 1985 PBS documentary series narrated by Martin Sheen, see Spaceflight (TV series). For the Sam Lazar album, see Space Flight (album). Part of a… … Wikipedia
Physical Sciences — ▪ 2009 Introduction Scientists discovered a new family of superconducting materials and obtained unique images of individual hydrogen atoms and of a multiple exoplanet system. Europe completed the Large Hadron Collider, and China and India took… … Universalium
Portal:Spaceflight — Wikipedia portals: Culture Geography Health History Mathematics Natural sciences People Philosophy Religion Society Technology The Spaceflight Portal … Wikipedia
Timeline of artificial satellites and space probes — This Timeline of artificial satellites and space probes includes unmanned spacecraft including technology demonstrators, observatories, lunar probes, and interplanetary probes. First satellites from each country are included. Not inclued are… … Wikipedia
space exploration — Investigation of the universe beyond Earth s atmosphere by means of manned and unmanned spacecraft. Study of the use of rockets for spaceflight began early in the 20th century. Germany s research on rocket propulsion in the 1930s led to… … Universalium
Space Race — For a discussion of all spaceflight programs to date, see History of spaceflight. For a list of key events, see Timeline of space exploration. For other uses of the term, see Space Race (disambiguation). A replica of Sputnik 1, the world s… … Wikipedia
Space colonization — Artist Les Bossinas 1989 concept of Mars mission Space colonization (also called space settlement, space humanization, or space habitation) is the concept of permanent human habitation outside of Earth. Although hypothetical at the present time,… … Wikipedia
Hayabusa — This article is about the spacecraft. For other uses, see Hayabusa (disambiguation). Hayabusa A computer rendering of Hayabusa above Itokawa s surface Operator … Wikipedia
Mir — This article is about the Soviet/Russian space station. For other uses, see Mir (disambiguation). Mir … Wikipedia
Spacecraft — Spaceship redirects here. For other uses, see Spaceship (disambiguation). More than 100 Russian Soyuz manned spacecraft (TMA version shown) have flown since 1967, originally for a Soviet manned lunar program, but currently supporting the… … Wikipedia
 1For shuttle flight, commander and pilot are listed first; for Soyuz flights, ISS commander is listed first.2Flight dates for shuttle and Shenzhou missions; Soyuz launch or return date for ISS missions.
1For shuttle flight, commander and pilot are listed first; for Soyuz flights, ISS commander is listed first.2Flight dates for shuttle and Shenzhou missions; Soyuz launch or return date for ISS missions.