- Sulfate minerals
-
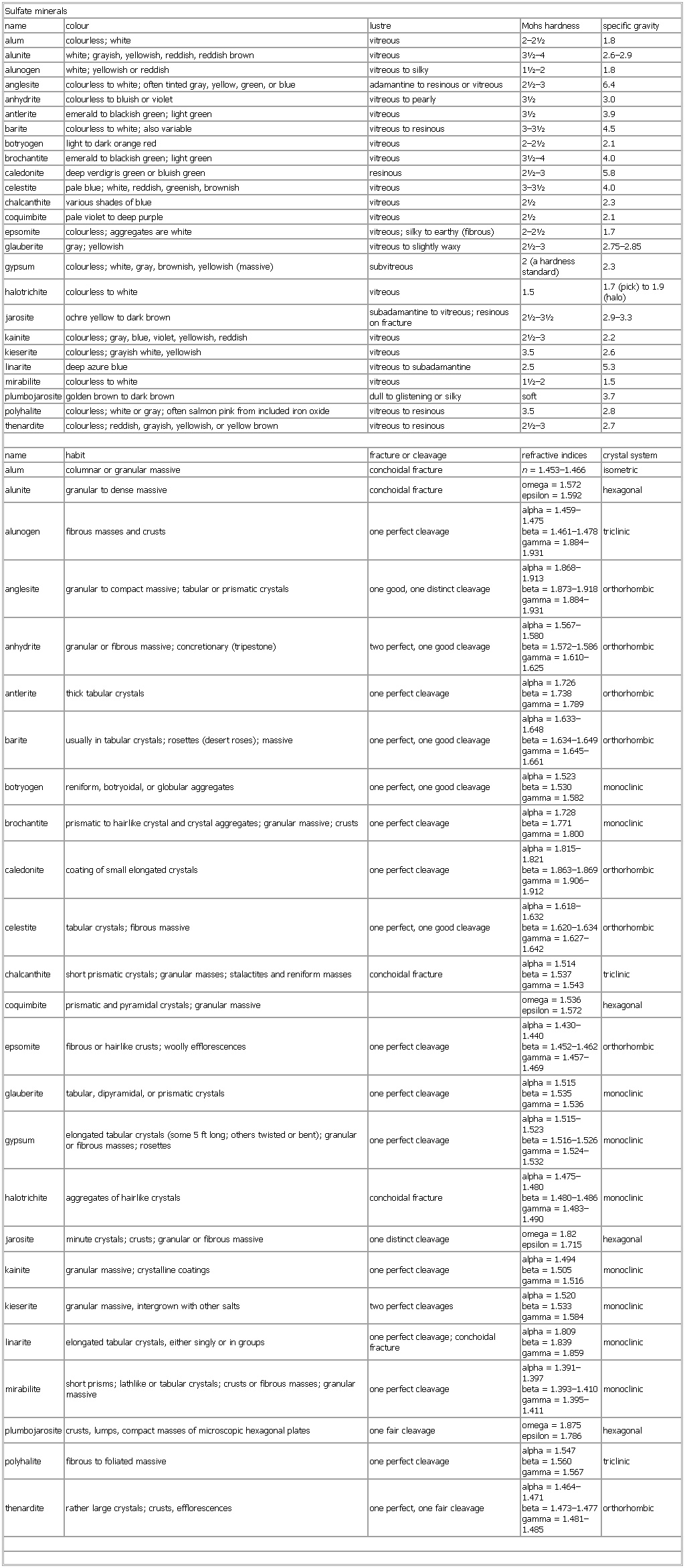
▪ TableSulfate mineralsname colour lustre Mohs hardness specific gravityalum colourless; white vitreous 2–2½ 1.8alunite white; grayish, yellowish, reddish, reddish brown vitreous 3½–4 2.6–2.9alunogen white; yellowish or reddish vitreous to silky 1½–2 1.8anglesite colourless to white; often tinted gray, yellow, green, or blue adamantine to resinous or vitreous 2½–3 6.4anhydrite colourless to bluish or violet vitreous to pearly 3½ 3.0antlerite emerald to blackish green; light green vitreous 3½ 3.9barite colourless to white; also variable vitreous to resinous 3–3½ 4.5botryogen light to dark orange red vitreous 2–2½ 2.1brochantite emerald to blackish green; light green vitreous 3½–4 4.0caledonite deep verdigris green or bluish green resinous 2½–3 5.8celestite pale blue; white, reddish, greenish, brownish vitreous 3–3½ 4.0chalcanthite various shades of blue vitreous 2½ 2.3coquimbite pale violet to deep purple vitreous 2½ 2.1glauberite gray; yellowish vitreous to slightly waxy 2½–3 2.75–2.85gypsum colourless; white, gray, brownish, yellowish (massive) subvitreous 2 (a hardness standard) 2.3jarosite ochre yellow to dark brown subadamantine to vitreous; resinous on fracture 2½–3½ 2.9–3.3kainite colourless; gray, blue, violet, yellowish, reddish vitreous 2½–3 2.2kieserite colourless; grayish white, yellowish vitreous 3.5 2.6linarite deep azure blue vitreous to subadamantine 2.5 5.3mirabilite colourless to white vitreous 1½–2 1.5plumbojarosite golden brown to dark brown dull to glistening or silky soft 3.7polyhalite colourless; white or gray; often salmon pink from included iron oxide vitreous to resinous 3.5 2.8thenardite colourless; reddish, grayish, yellowish, or yellow brown vitreous to resinous 2½–3 2.7name habit fracture or cleavage refractive indices crystal systemalum columnar or granular massive conchoidal fracture n = 1.453–1.466 isometricalunite granular to dense massive conchoidal fracture omega = 1.572epsilon = 1.592 hexagonalalunogen fibrous masses and crusts one perfect cleavage alpha = 1.459–1.475beta = 1.461–1.478gamma = 1.884–1.931 triclinicanglesite granular to compact massive; tabular or prismatic crystals one good, one distinct cleavage alpha = 1.868–1.913beta = 1.873–1.918gamma = 1.884–1.931 orthorhombicanhydrite granular or fibrous massive; concretionary (tripestone) two perfect, one good cleavage alpha = 1.567–1.580beta = 1.572–1.586gamma = 1.610–1.625 orthorhombicantlerite thick tabular crystals one perfect cleavage alpha = 1.726beta = 1.738gamma = 1.789 orthorhombicbarite usually in tabular crystals; rosettes (desert roses); massive one perfect, one good cleavage alpha = 1.633–1.648beta = 1.634–1.649gamma = 1.645–1.661 orthorhombicbotryogen reniform, botryoidal, or globular aggregates one perfect, one good cleavage alpha = 1.523beta = 1.530gamma = 1.582 monoclinicbrochantite prismatic to hairlike crystal and crystal aggregates; granular massive; crusts one perfect cleavage alpha = 1.728beta = 1.771gamma = 1.800 monocliniccaledonite coating of small elongated crystals one perfect cleavage alpha = 1.815–1.821beta = 1.863–1.869gamma = 1.906–1.912 orthorhombiccelestite tabular crystals; fibrous massive one perfect, one good cleavage alpha = 1.618–1.632beta = 1.620–1.634gamma = 1.627–1.642 orthorhombicchalcanthite short prismatic crystals; granular masses; stalactites and reniform masses conchoidal fracture alpha = 1.514beta = 1.537gamma = 1.543 tricliniccoquimbite prismatic and pyramidal crystals; granular massive omega = 1.536epsilon = 1.572 hexagonalepsomite fibrous or hairlike crusts; woolly efflorescences one perfect cleavage alpha = 1.430–1.440beta = 1.452–1.462gamma = 1.457–1.469 orthorhombicglauberite tabular, dipyramidal, or prismatic crystals one perfect cleavage alpha = 1.515beta = 1.535gamma = 1.536 monoclinicgypsum elongated tabular crystals (some 5 ft long; others twisted or bent); granular or fibrous masses; rosettes one perfect cleavage alpha = 1.515–1.523beta = 1.516–1.526gamma = 1.524–1.532 monoclinichalotrichite aggregates of hairlike crystals conchoidal fracture alpha = 1.475–1.480beta = 1.480–1.486gamma = 1.483–1.490 monoclinicjarosite minute crystals; crusts; granular or fibrous massive one distinct cleavage omega = 1.82epsilon = 1.715 hexagonalkainite granular massive; crystalline coatings one perfect cleavage alpha = 1.494beta = 1.505gamma = 1.516 monoclinickieserite granular massive, intergrown with other salts two perfect cleavages alpha = 1.520beta = 1.533gamma = 1.584 monocliniclinarite elongated tabular crystals, either singly or in groups one perfect cleavage; conchoidal fracture alpha = 1.809beta = 1.839gamma = 1.859 monoclinicmirabilite short prisms; lathlike or tabular crystals; crusts or fibrous masses; granular massive one perfect cleavage alpha = 1.391–1.397beta = 1.393–1.410gamma = 1.395–1.411 monoclinicplumbojarosite crusts, lumps, compact masses of microscopic hexagonal plates one fair cleavage omega = 1.875epsilon = 1.786 hexagonalpolyhalite fibrous to foliated massive one perfect cleavage alpha = 1.547beta = 1.560gamma = 1.567 triclinicthenardite rather large crystals; crusts, efflorescences one perfect, one fair cleavage alpha = 1.464–1.471beta = 1.473–1.477gamma = 1.481–1.485 orthorhombicSee as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
