Properties of the alkali metals
- Properties of the alkali metals
-
Properties of the alkali metals
colour of element silver silver silver silver silver —
density at 20 degrees Celsius (grams per cubic centimetre) 0.534 0.971 0.862 1.532 1.873 —
volume increase on melting (
percent)
1.
51 2.
63 2.
81 2.
54 2.
66 —
mass number of most common isotopes (
terrestrial abundance,
percent)
7 (
92.
6),
6 (
7.
4)
23 (
100)
39 (
93.
1),
41 (
6.
88),
40 (
0.
0119)
85 (
72.
15),
87 (
27.
85)
133 (
100) —
colour imparted to flame red yellow violet dark red blue —
main spectral emission lines (
wavelength,
angstroms)
6,
708;
6,
104 5,
890;
5,
896 7,
699;
7,
665 4,
216;
4,
202 4,
593;
4,
555 —
heat of fusion
(calories per mole) 717 621 558 523 500 —
electrical resistivity at 20–
25 degrees Celsius (
microhm centimetres)
9.
4 4.
7 7 12 20 —
(cgs unit) 14.2 (10−6) 16.0 (10−6) 20.8
(10−6) 17.0 (10−6) 29.0 (10−6) —
crystal structure body-centred cubic body-centred cubic body-centred cubic body-centred cubic body-centred cubic —
radius
atomic
(angstroms) 1.52 1.86 2.27 2.48 2.65 —
ionic (+1 ion,
angstroms) 0.9 1.16 1.52 1.66 1.81 1.94
bond,
angstroms) 1.225 1.572 2.025 2.16 2.35 —
oxidation potential for oxidation from the 0 to +1 oxidation state at 25 degrees Celsius (volts) 3.04 2.71 2.92 2.92 2.92 —
See as table: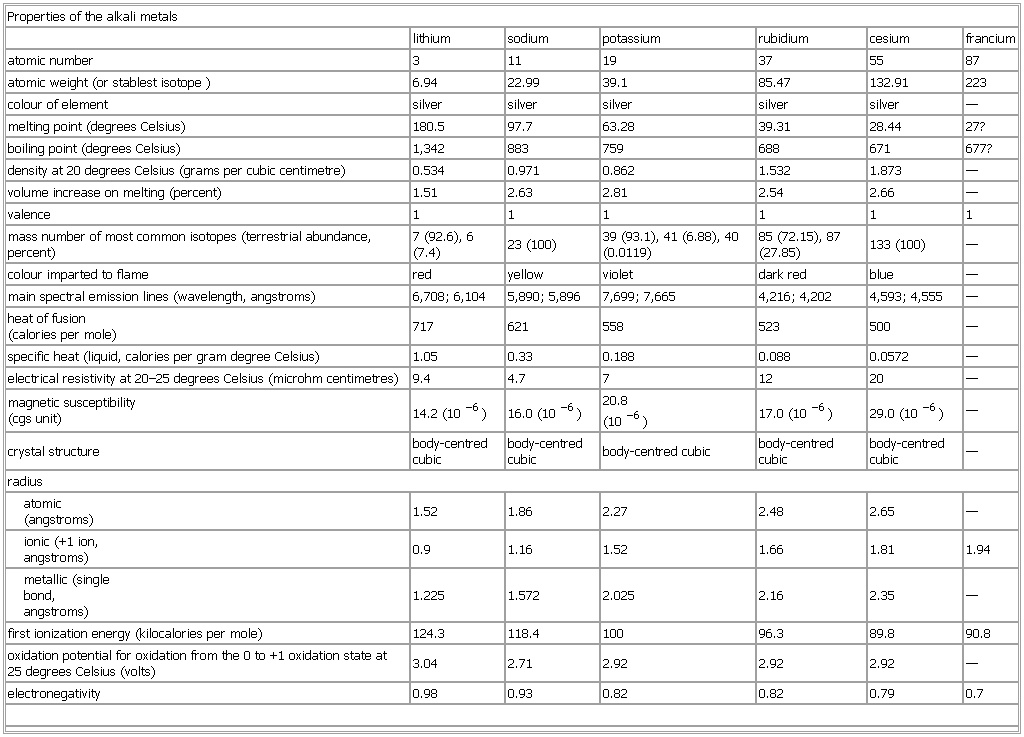
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
alkali metal — Chem. any of the group of univalent metals including potassium, sodium, lithium, rubidium, cesium, and francium, whose hydroxides are alkalis. [1880 85] * * * Any of the six chemical elements in the leftmost group of the periodic table (lithium,… … Universalium
Alkali metal — Group → 1 ↓ Period 2 3 Li 3 … Wikipedia
Properties of water — H2O and HOH redirect here. For other uses, see H2O (disambiguation) and HOH (disambiguation). This article is about the physical and chemical properties of pure water. For general discussion and its distribution and importance in life, see Water … Wikipedia
alkali — n. (pl. alkalis) 1 a any of a class of substances that liberate hydroxide ions in water, usu. form caustic or corrosive solutions, turn litmus blue, and have a pH of more than 7, e.g. caustic soda. b any other substance with similar but weaker… … Useful english dictionary
History of the periodic table — The history of the periodic table reflects over a century of growth in the understanding of chemical properties, and culminates with the publication of the first actual periodic table by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869.[1] While Mendeleev built upon… … Wikipedia
alkali — 1. A strongly basic substance yielding hydroxide ions (OH− in solution); e.g., sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide. 2. SYN: base (3). 3. SYN: a. metal. [Ar., al, the, + qaliy, soda ash] caustic a … Medical dictionary
Refractory metals — are a class of metals that are extraordinarily resistant to heat and wear. Refractory metals are said to be poorly resistant to oxidation and corrosion. [UFL EMA 6625: Advanced Metal Processing, Summer 2008, Lecture 09] These properties make them … Wikipedia
Abundance of the chemical elements — Estimated proportions of matter, dark matter and dark energy in the universe. Only the fraction of the mass and energy in the universe labeled atoms is composed of chemical elements. The abundance of a chemical element measures how relatively… … Wikipedia
Vapor pressures of the elements (data page) — … Wikipedia
Heavy metals — Metal Met al (? or ?; 277), n. [F. m[ e]tal, L. metallum metal, mine, Gr. ? mine; cf. Gr. ? to search after. Cf. {Mettle}, {Medal}.] 1. (Chem.) An elementary substance, as sodium, calcium, or copper, whose oxide or hydroxide has basic rather than … The Collaborative International Dictionary of English

