Dry bulk densities for various rock types
- Dry bulk densities for various rock types
-
Dry bulk densities for various rock types
rock type number of samples mean (grams per cubic cm) standard deviation mode (grams per cubic cm) median (grams per cubic cm)
all rocks 1,647 2.73 0.26 2.65 2.86
andesite 197 2.65 0.13 2.58 2.66
basalt 323 2.74 0.47 2.88 2.87
diorite 68 2.86 0.12 2.89 2.87
dolerite (
diabase) 224 2.89 0.13 2.96 2.90
gabbro 98 2.95 0.14 2.99 2.97
granite 334 2.66 0.06 2.66 2.66
quartz porphyry 76 2.62 0.06 2.60 2.62
rhyolite 94 2.51 0.13 2.60 2.49
syenite 93 2.70 0.10 2.67 2.68
trachyte 71 2.57 0.10 2.62 2.57
sandstone 107 2.22 0.23 2.22 2.22
Source: After data from H.S. Washington (1917) and R.J. Piersol, L.E. Workman, and M.C. Watson (1940) as compiled by Gary R. Olhoeft and Gordon R. Johnson in Robert S. Carmichael, ed., Handbook of Physical Properties of Rocks, vol. III, CRC Press, Inc. (1984).
See as table: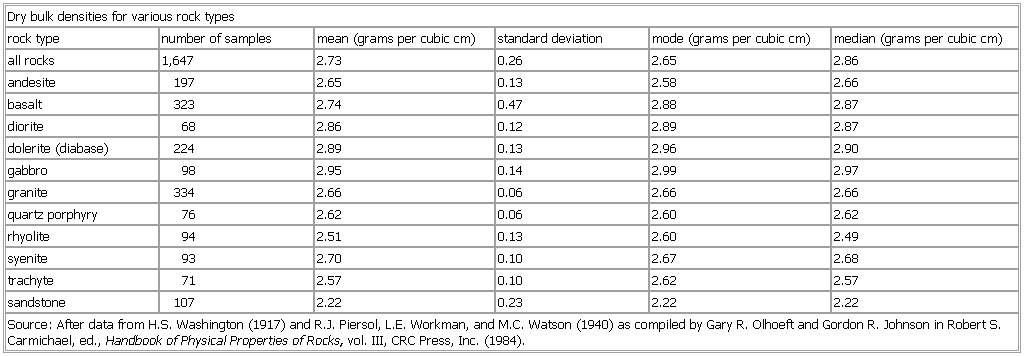
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
rock — rock1 rockless, adj. rocklike, adj. /rok/, n. 1. a large mass of stone forming a hill, cliff, promontory, or the like. 2. Geol. a. mineral matter of variable composition, consolidated or unconsolidated, assembled in masses or considerable… … Universalium
Rock — /rok/, n. a male given name. * * * I In geology, a naturally occurring and coherent aggregate of minerals. The three major classes of rock igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic are based on the processes that formed them. These three classes are… … Universalium
Types of concrete — There are many types of concrete, variations of installation, composition, finish and performance characteristics. A highway paved with concrete … Wikipedia
metamorphic rock — Any of a class of rocks that result from the alteration of preexisting rocks in response to changing geological conditions, including variations in temperature, pressure, and mechanical stress. The preexisting rocks may be igneous, sedimentary,… … Universalium
India — /in dee euh/, n. 1. Hindi, Bharat. a republic in S Asia: a union comprising 25 states and 7 union territories; formerly a British colony; gained independence Aug. 15, 1947; became a republic within the Commonwealth of Nations Jan. 26, 1950.… … Universalium
Asia — /ay zheuh, ay sheuh/, n. a continent bounded by Europe and the Arctic, Pacific, and Indian oceans. 2,896,700,000; ab. 16,000,000 sq. mi. (41,440,000 sq. km). * * * I Largest continent on Earth. It is bounded by the Arctic Ocean, the Pacific Ocean … Universalium
china — /chuy neuh/, n. 1. a translucent ceramic material, biscuit fired at a high temperature, its glaze fired at a low temperature. 2. any porcelain ware. 3. plates, cups, saucers, etc., collectively. 4. figurines made of porcelain or ceramic material … Universalium
China — /chuy neuh/, n. 1. People s Republic of, a country in E Asia. 1,221,591,778; 3,691,502 sq. mi. (9,560,990 sq. km). Cap.: Beijing. 2. Republic of. Also called Nationalist China. a republic consisting mainly of the island of Taiwan off the SE coast … Universalium
Africa — /af ri keuh/, n. 1. a continent S of Europe and between the Atlantic and Indian oceans. 551,000,000; ab. 11,700,000 sq. mi. (30,303,000 sq. km). adj. 2. African. * * * I Second largest continent on Earth. It is bounded by the Mediterranean Sea,… … Universalium
Earth Sciences — ▪ 2009 Introduction Geology and Geochemistry The theme of the 33rd International Geological Congress, which was held in Norway in August 2008, was “Earth System Science: Foundation for Sustainable Development.” It was attended by nearly… … Universalium

