Some properties of normal hydrogen and deuterium
- Some properties of normal hydrogen and deuterium
-
Some properties of normal hydrogen and deuterium
normal hydrogen deuterium
Atomic hydrogen
atomic number 1 1
atomic weight 1.0080 2.0141
ionization potential 13.595 electron volts 13.600 electron volts
electron affinity 0.7542 electron volts 0.754 electron volts
nuclear spin 1/2 1
nuclear magnetic moment (nuclear magnetons) 2.7927 0.8574
nuclear quadrupole moment 0 2.77(10−27) square centimetres
electronegativity (
Pauling)
2.
1 Some properties of normal hydrogen and deuterium2.
1
Molecular hydrogen
bond distance 0.7416 angstrom 0.7416 angstrom
dissociation energy (25 degrees C) 104.19 kilocalories per mole 105.97 kilocalories per mole
ionization potential 15.427 electron volts 15.457 electron volts
density of solid 0.08671 gram per cubic centimetre 0.1967 gram per cubic centimetre
melting point −259.20 degrees Celsius −254.43 degrees Celsius
heat of fusion 28 calories per mole 47 calories per mole
density of liquid 0.07099
(−252.78 degrees) 0.1630
(−249.75 degrees)
boiling point −252.77 degrees Celsius −249.49 degrees Celsius
heat of vaporization 216 calories per mole 293 calories per mole
critical temperature −240.0 degrees Celsius −243.8 degrees Celsius
critical pressure 13.0 atmospheres 16.4 atmospheres
critical density 0.0310 gram per cubic centimetre 0.0668 gram per cubic centimetre
heat of combustion to water (g) −57.796 kilocalories per mole −59.564 kilocalories per mole
See as table: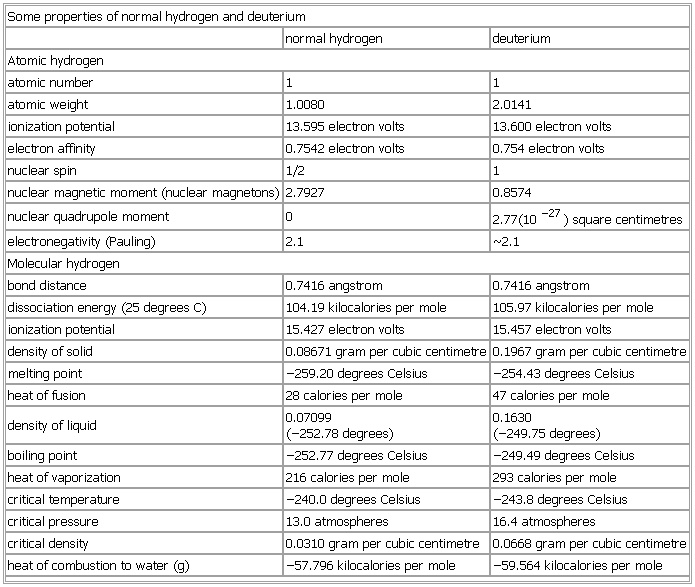
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
hydrogen — /huy dreuh jeuhn/, n. a colorless, odorless, flammable gas that combines chemically with oxygen to form water: the lightest of the known elements. Symbol: H; at. wt.: 1.00797; at. no.: 1; density: 0.0899 g/l at 0°C and 760 mm pressure. [1785 95;… … Universalium
Deuterium — Hydrogen 2 Full table General Name, symbol deuterium, 2H or D Neutrons 1 … Wikipedia
Hydrogen peroxide — IUPAC name … Wikipedia
Hydrogen — This article is about the chemistry of hydrogen. For the physics of atomic hydrogen, see Hydrogen atom. For other meanings, see Hydrogen (disambiguation). ← hydrogen → helium … Wikipedia
Properties of water — H2O and HOH redirect here. For other uses, see H2O (disambiguation) and HOH (disambiguation). This article is about the physical and chemical properties of pure water. For general discussion and its distribution and importance in life, see Water … Wikipedia
Metallic hydrogen — Some gas giants have metallic hydrogen in their centers Metallic hydrogen is a state of hydrogen which results when it is sufficiently compressed and undergoes a phase transition; it is an example of degenerate matter. Solid metallic hydrogen is… … Wikipedia
Hydrogen sulfide — Systematic name … Wikipedia
Mathematics and Physical Sciences — ▪ 2003 Introduction Mathematics Mathematics in 2002 was marked by two discoveries in number theory. The first may have practical implications; the second satisfied a 150 year old curiosity. Computer scientist Manindra Agrawal of the… … Universalium
List of fictional elements, materials, isotopes and atomic particles — This list contains chemical elements, materials, isotopes or (sub)atomic particle that exist primarily in works of fiction (usually fantasy or science fiction). No actual periodic elements end in ite , though many minerals have names with this… … Wikipedia
Spin isomers of hydrogen — Spin Isomers of Molecular Hydrogen Molecular hydrogen occurs in two isomeric forms, one with its two proton spins aligned parallel (orthohydrogen), the other with its two proton spins aligned antiparallel (parahydrogen).[1] At room temperature… … Wikipedia

