Cation-exchange capacities and specific surface areas of clay minerals
- Cation-exchange capacities and specific surface areas of clay minerals
-
Cation-exchange capacities and specific surface areas of clay minerals
mineral cation-exchange capacity at pH 7 (milliequivalents per 100 grams) specific surface area (square metre per gram)
kaolinite 3–15 5–40
illite 10–40 10–100
chlorite 10–40 10–55
vermiculite 100–150 760*
smectite 80–120 40–800
palygorskite-sepiolite 3–20 40–180
allophane 30–135 2,200*
imogolite 20–30 1,540*
*Upper limit of estimated values.
See as table: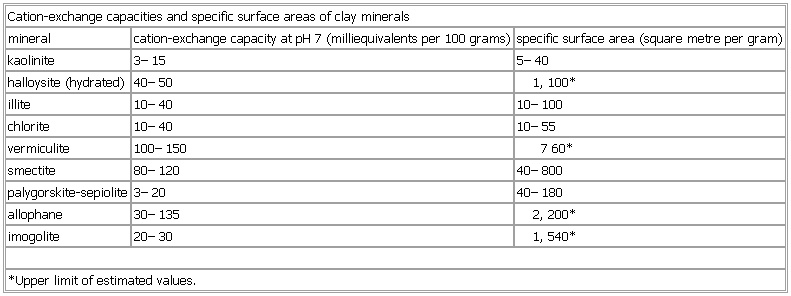
* * *
Universalium.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
clay mineral — any of a group of hydrous aluminum silicate minerals, as kaolinite, illite, and montmorillonite, that constitute the major portion of most clays. [1945 50] * * * Any of a group of important hydrous aluminum silicates with a layered structure and… … Universalium
Western Africa — ▪ region, Africa Introduction region lying south of the Sahara and east and north of the Atlantic Ocean. It is latitudinally divided into two parallel belts of land: the western portion of the Sudan, a geographic area that stretches across… … Universalium

