- Some properties of the alkaline metals
-
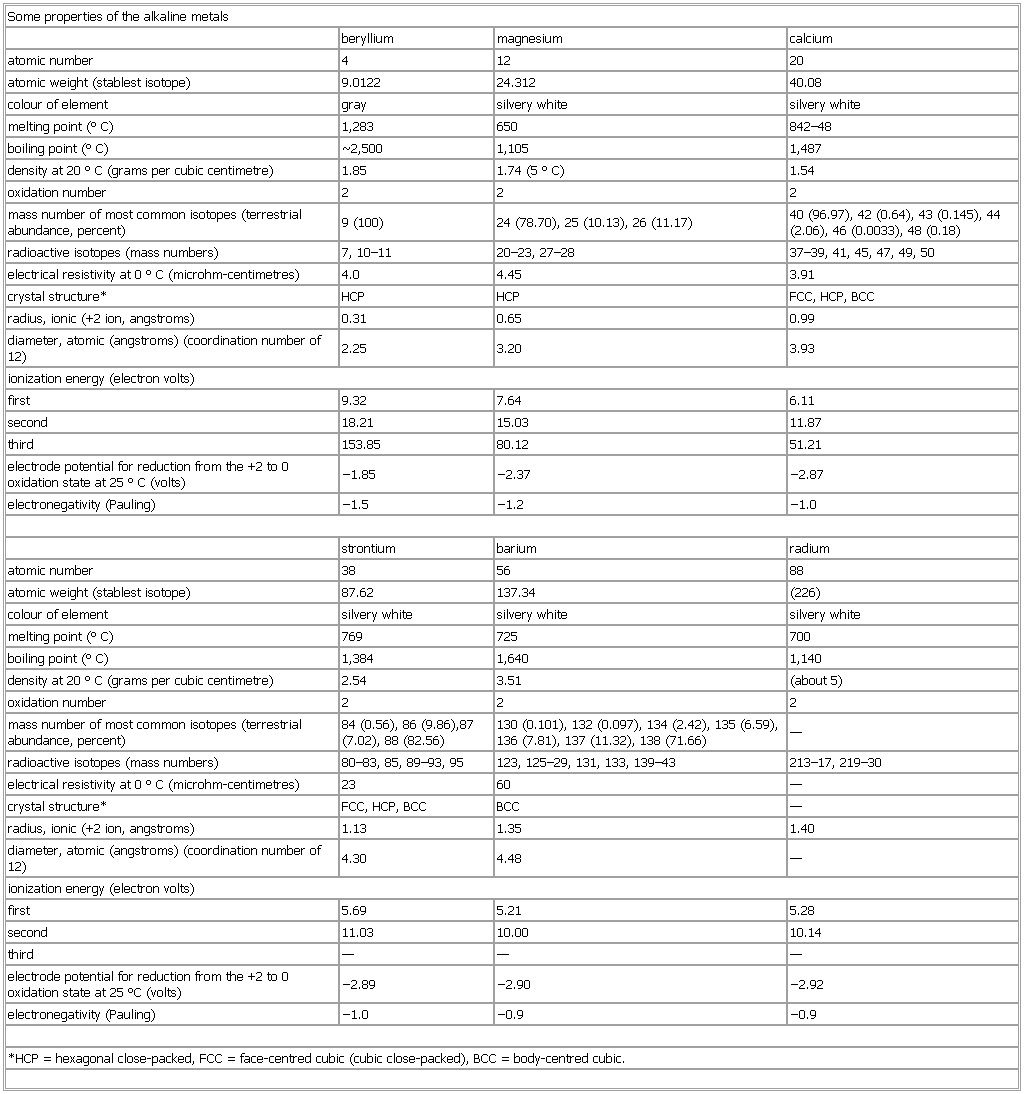
▪ TableSome properties of the alkaline metalsberyllium magnesium calciumatomic number 4 12 20atomic weight (stablest isotope) 9.0122 24.312 40.08colour of element gray silvery white silvery whitemelting point (°C) 1,283 650 842–48boiling point (°C) Some properties of the alkaline metals2,500 1,105 1,487density at 20 °C (grams per cubic centimetre) 1.85 1.74 (5 °C) 1.54oxidation number 2 2 2mass number of most common isotopes (terrestrial abundance, percent) 9 (100) 24 (78.70), 25 (10.13), 26 (11.17) 40 (96.97), 42 (0.64), 43 (0.145), 44 (2.06), 46 (0.0033), 48 (0.18)radioactive isotopes (mass numbers) 7, 10–11 20–23, 27–28 37–39, 41, 45, 47, 49, 50electrical resistivity at 0 °C (microhm-centimetres) 4.0 4.45 3.91crystal structure* HCP HCP FCC, HCP, BCCradius, ionic (+2 ion, angstroms) 0.31 0.65 0.99diameter, atomic (angstroms) (coordination number of 12) 2.25 3.20 3.93ionization energy (electron volts)first 9.32 7.64 6.11second 18.21 15.03 11.87third 153.85 80.12 51.21electrode potential for reduction from the +2 to 0 oxidation state at 25 °C (volts) −1.85 −2.37 −2.87electronegativity (Pauling) −1.5 −1.2 −1.0strontium barium radiumatomic number 38 56 88atomic weight (stablest isotope) 87.62 137.34 (226)colour of element silvery white silvery white silvery whitemelting point (°C) 769 725 700boiling point (°C) 1,384 1,640 1,140density at 20 °C (grams per cubic centimetre) 2.54 3.51 (about 5)oxidation number 2 2 2mass number of most common isotopes (terrestrial abundance, percent) 84 (0.56), 86 (9.86),87 (7.02), 88 (82.56) 130 (0.101), 132 (0.097), 134 (2.42), 135 (6.59), 136 (7.81), 137 (11.32), 138 (71.66) —radioactive isotopes (mass numbers) 80–83, 85, 89–93, 95 123, 125–29, 131, 133, 139–43 213–17, 219–30electrical resistivity at 0 °C (microhm-centimetres) 23 60 —crystal structure* FCC, HCP, BCC BCC —radius, ionic (+2 ion, angstroms) 1.13 1.35 1.40diameter, atomic (angstroms) (coordination number of 12) 4.30 4.48 —ionization energy (electron volts)first 5.69 5.21 5.28second 11.03 10.00 10.14third — — —electrode potential for reduction from the +2 to 0 oxidation state at 25 °C (volts) −2.89 −2.90 −2.92electronegativity (Pauling) −1.0 −0.9 −0.9*HCP = hexagonal close-packed, FCC = face-centred cubic (cubic close-packed), BCC = body-centred cubic.See as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
