- Common fatty acids in foods
-
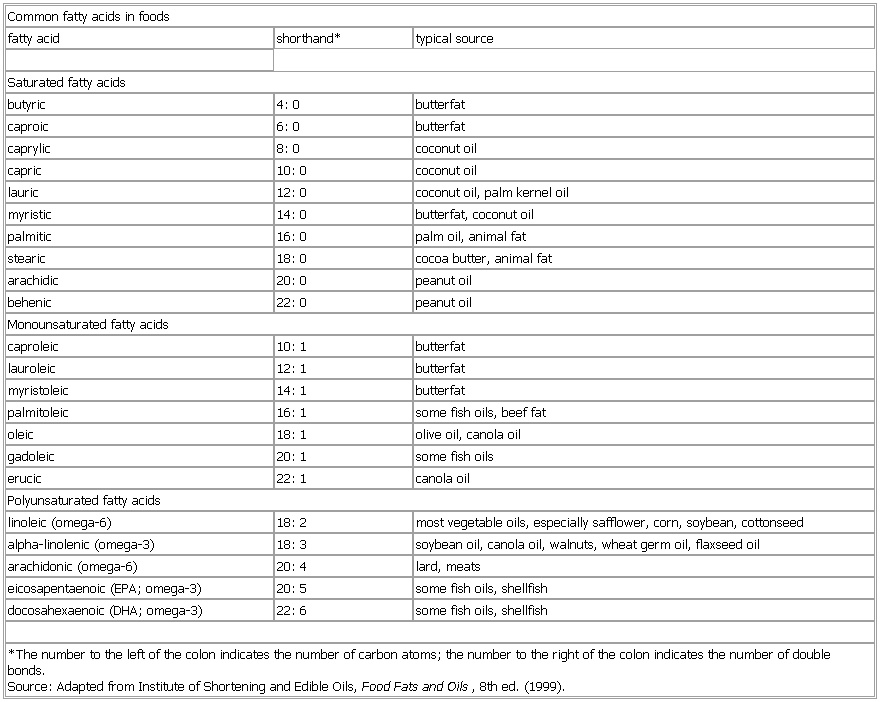
▪ TableCommon fatty acids in foodsfatty acid shorthand* typical sourceSaturated fatty acidsbutyric 4:0 butterfatcaproic 6:0 butterfatcaprylic 8:0 coconut oilcapric 10:0 coconut oillauric 12:0 coconut oil, palm kernel oilmyristic 14:0 butterfat, coconut oilpalmitic 16:0 palm oil, animal fatstearic 18:0 cocoa butter, animal fatarachidic 20:0 peanut oilbehenic 22:0 peanut oilMonounsaturated fatty acidscaproleic 10:1 butterfatlauroleic 12:1 butterfatmyristoleic 14:1 butterfatpalmitoleic 16:1 some fish oils, beef fatoleic 18:1 olive oil, canola oilgadoleic 20:1 some fish oilserucic 22:1 canola oilPolyunsaturated fatty acidslinoleic (omega-6) 18:2 most vegetable oils, especially safflower, corn, soybean, cottonseedalpha-linolenic (omega-3) 18:3 soybean oil, canola oil, walnuts, wheat germ oil, flaxseed oilarachidonic (omega-6) 20:4 lard, meatseicosapentaenoic (EPA; omega-3) 20:5 some fish oils, shellfishdocosahexaenoic (DHA; omega-3) 22:6 some fish oils, shellfish*The number to the left of the colon indicates the number of carbon atoms; the number to the right of the colon indicates the number of double bonds.Source: Adapted from Institute of Shortening and Edible Oils, Food Fats and Oils, 8th ed. (1999).See as table:
* * *
Universalium. 2010.
